OpenAI just crossed 400 million weekly active users, which is close to 5% of the world’s population. This means that they are growing at an astounding 50 million weekly active users per month, just 2 months ago OpenAI announced that they have 300 million weekly active users. The growth is accelerating, and OpenAI predicts they will reach 1 billion weekly active users by the end of the year. I find myself using ChatGPT, Claude and Perplexity more and more myself as the weeks go by, and as the tools themselves get better and better they really start to feel like an extension of my brain, instead of being just “another application”. AI has completely changed the way I do my work on a daily basis, and it’s about to change the daily life of every person on the planet with Internet access.
The next step of the AI evolution is agentic. Just last week Google launched their AI Co-Scientist Research Assistant that replicated research that has taken 10 years in just two days. The results were so outstandingly good that José Penadés who led the original research team initially suspected that Google had access to his private files on his local computer. We are starting to see a clear trend on how research agents are being rolled out on a large scale, and it won’t be many months until we see software development agents being available to hire as freelance developers. We just need a slight quality bump in coding performance, and I am cautiously optimistic we will get this with GPT-4.5 and Claude 4. The year 2025 is really starting out amazingly well!
Thank you for being a Tech Insights subscriber!
THIS WEEK’S NEWS:
- Google launches AI Co-Scientist Research Assistant
- Google’s AI Co-Scientist Solved 10 Years of Research in Two Days
- Grok 3 Launch: This Is Not the Model You Are Looking For
- GitHub Copilot Launches New Code Completion Based on GPT-4o Mini
- Microsoft Launches BioEmu-1 to Accelerate Protein Structure Research
- Arc Institute and Nvidia Launches Evo 2 – AI Model for Biology
- Microsoft unveils Muse Generative AI Model for Video Game Prototyping
- OpenAI Introduces New Software Engineering Benchmark SWE-Lancer
- Perplexity Remakes DeepSeek-R1 Reasoning Model
- Pika Labs Launches Pikaswaps – Video Object Replacement Tool
- Sakana AI Releases AI CUDA Engineer – 100x Faster Turned Out to be 3x Slower
Google launches AI Co-Scientist Research Assistant
https://research.google/blog/accelerating-scientific-breakthroughs-with-an-ai-co-scientist
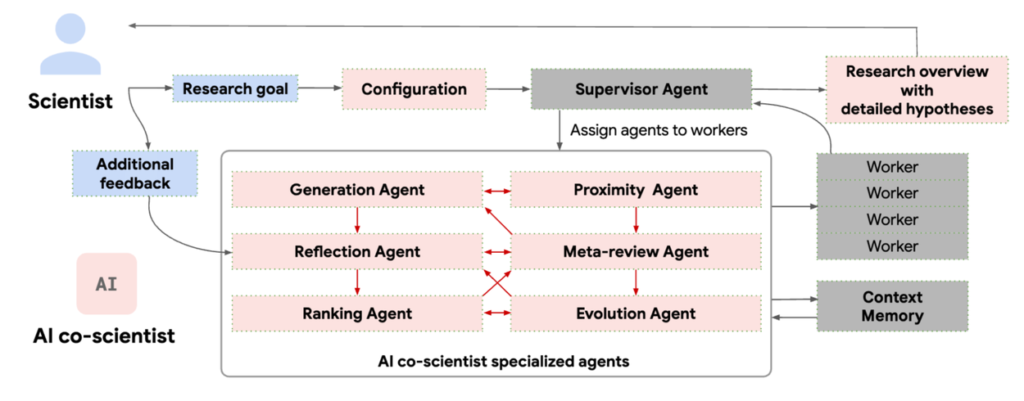
The News:
- Google just launched “AI co-scientist”, a multi-agent AI system built on Gemini 2.0 that helps scientists generate research hypotheses and experimental protocols. In an early test, the system replicated a decade-long research finding in just two days (see more below).
- The system works by having scientists input research goals in natural language. Six specialized AI agents then work together to generate, evaluate, and refine hypotheses while accessing scientific literature and databases.
- Scientists can interact with the system by providing feedback and their own ideas, making it a collaborative tool rather than an automation replacement.
- Initial testing shows 80%+ accuracy on expert-level benchmarks, outperforming both existing AI models and human experts.
- Google is rolling out access through a Trusted Tester Program, targeting research organizations globally for trials across multiple scientific domains.
My take: This is still in its very early stages but the way it is designed is yet another win for agentic systems. The system is coordinated by a Supervisor agent that manages the overall research plan configuration and allocates resources to other specialized agents. These agents are called generation, reflection, ranking, evolution, proximity and meta-review. The agents then engage in a tournament-style evaluation system where they generate multiple hypotheses and research proposals, debate these ideas among themselves, use Elo-based ranking to evaluate and prioritize hypotheses through pairwise comparisons, and continuously refine ideas through iterative improvements. This continues to run for hours and days, until a consensus can be made. Right now only 20 principal researchers have access to this tool, but think ahead a few months, maybe a year, and I am willing to bet that everyone will have their own “AI co-scientist” available for any kind of work.
Google’s AI Co-Scientist Solved 10 Years of Research in Two Days
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyz6e9edy3o
The News:
- Google’s new “co-scientist” AI tool solved a complex antimicrobial resistance problem in just two days, matching conclusions that took researchers at Imperial College London ten years to develop and prove.
- During its trial with Imperial College London, the AI Co-Scientist analyzed over 28,000 studies, proposed 143 mechanisms for bacterial DNA transfer, and ranked the correct hypothesis as its top result – all within two days. The AI correctly generated the hypothesis about how superbugs form “tails” from different viruses to spread between species, despite having no access to the unpublished research.
- Beyond replicating the original findings, the AI proposed four additional plausible hypotheses, including one novel approach that researchers are now investigating.
- Professor José Penadés, who led the original research, was so surprised by the AI’s accuracy that he initially suspected Google had accessed his computer files.
- The discovery focuses on understanding how bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, a critical global health concern projected to cause millions of deaths by 2050.
My take: If there is any indication where we are heading when it comes to all types of future research, this is it. Thanks to the revolutionary new AI co-scientist released by Google last week, any company can now have their own private research team that works tirelessly day and night at an efficiency unparalleled by humans. If you are currently working in a company that specializes in research reports as a business I think you would be wise to reconsider your career choice pretty quickly.
Grok 3 Launch: This Is Not the Model You Are Looking For
The News:
- xAI released Grok 3, a new AI model trained on massive computing power (200,000 GPUs) that introduces features like Think Mode for step-by-step reasoning and Big Brain Mode for computation-heavy tasks.
- The model claimed superior performance in mathematics and science, scoring 93.3% on AIME 2025 and 84.6% on graduate-level expert reasoning (GPQA).
- Access to Grok 3 was initially limited to X Premium+ subscribers, and the cost for a X Premium+ subscriptions was raised from $22 to $40 / month. The advanced features like DeepSearch and Think Mode required paying an additional $30/month for a version called “SuperGrok”.
- A few days later, on February 20, Elon Musk announced free access for everyone “for a short time”.
What you might have missed (1): According to Boris Power, Head of Applied Research at OpenAI, “the grok team cheated and deceived in evals. o3-mini is better in every eval compared to grok 3.”
What you might have missed (2): A typical benchmark for checking how good a model is at coding is the “bouncing ball” test. As reported by numerous people Grok 3 fails this test completely, and is actually much worse than Claude 3.5 launched in June last year at most coding. It just shows how little these hand-picked benchmark results really mean in practice.
My take: I think very few of us are surprised with all the drama surrounding the Grok 3 launch. The model is clearly rushed, for what purpose I don’t really know. xAI did however prove that creating a good foundation model is not just about buying tons of NVIDIA cards and stacking them in large computer halls. Like most engineering it takes calendar time, and it’s not often 100 engineers can do the work of 10 experts if the work itself needs reflection and iterative collaboration. Many people will see the launch of Grok 3 as proof that we are stagnating in AI development, but I believe that is wrong. Just hang in there for GPT-4.5, Claude 4 and GPT-5, I believe will be worth it.
Read more:
- Andrej Karpathy on X: “I was given early access to Grok 3 earlier today, making me I think one of the first few who could run a quick vibe check.”
- Who’s Behind xAI Grok 3, Elon Musk’s ‘Maximally Truth-Seeking A.I.” | Observer
- Did xAI Manipulate Grok-3 Benchmarks & Reasoning Capabilities? – Geeky Gadgets
GitHub Copilot Launches New Code Completion Based on GPT-4o Mini

The News:
- GitHub launched a new code completion model called GPT-4o Copilot that improves code completion speed and accuracy. The model is available in public preview for Visual Studio Code users.
- The model builds on the GPT-4o mini architecture and includes training on over 275,000 high-quality public repositories across 30+ programming languages, resulting in more relevant and accurate code suggestions. The model has a context window of 128K tokens and supports up to 16K output tokens per request.
- The update supports a wide range of programming languages including Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Ruby, Go, C++, C#, Java, PHP, Swift, and Rust. It is currently available for VS Code users, with JetBrains IDE support coming soon.
My take: GitHub Copilot is quickly catching up to Cursor IDE which is already packed with custom models. From what I can see there are just two main features missing in Copilot: Prompt caching for performance and a local model for code merging. Once it gets those two features I think I would feel equally at home in Visual Studio Code + Copilot as with Cursor. And for all you Java and C# users, this is the update you have been waiting for. We finally have a good code completion model with good support for C++, C# and Java.
Read more:
Microsoft Launches BioEmu-1 to Accelerate Protein Structure Research
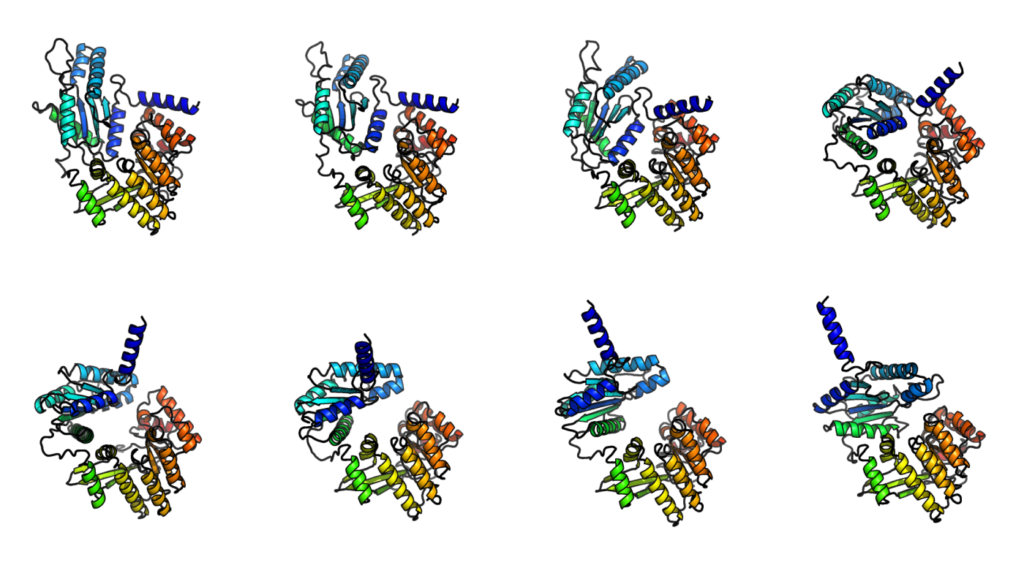
The News:
- Microsoft Research just launched BioEmu-1, an AI model that predicts how proteins move and change shape over time.
- Unlike AlphaFold, which predicts a single, static protein structure, BioEmu-1 generates thousands of conformations within hours using a single GPU. This makes it 10,000 – 100,000 times faster than traditional simulation methods.
- BioEmu-1 helps identify “cryptic pockets” – hidden binding sites that only appear when proteins shift shape, which is crucial for drug discovery. Combining AlphaFold’s static predictions with BioEmu-1’s dynamic modeling gives scientists a more complete view of protein behavior.
My take: Understanding how proteins move is just as important as knowing their shape. BioEmu-1 fills a gap in protein modeling by enabling large-scale dynamic simulations, which could lead to better drug designs, especially for diseases where proteins mutate or interact unpredictably. Instead of waiting weeks for simulations, researchers can now test ideas in hours, accelerating breakthroughs in drug discovery and disease research. Really impressive work by Microsoft, and it won’t be long now until we see the results of this amazing work.
Arc Institute and Nvidia Launches Evo 2 – AI Model for Biology
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/evo-2-biomolecular-ai
The News:
- Evo 2 is a new AI foundation model that can analyze and generate DNA sequences across all forms of life, trained on genetic data from over 128,000 different organisms including bacteria, plants, and humans.
- The model demonstrates 90% accuracy in identifying harmful mutations in genes like BRCA1 (breast cancer gene), potentially accelerating drug development and disease research.
- Arc is making Evo 2 freely available through NVIDIA’s BioNeMo platform, allowing researchers worldwide to use and build on the tech.
My take: Compared to AlphaFold and BioEmu-1 mentioned above that focus only on proteins, Evo 2 can analyze entire genomes such as DNA, RNA, and proteins simultaneously. This makes it much broader in scope than AlphaFold, which predicts single protein structures, or BioEmu, which models protein dynamics. You can see these models as complements where Evo 2 generates novel proteins or CRISPR systems, while AlphaFold predicts their structures. BioEmu then adds insights into protein flexibility and motion, useful for drug discovery. It’s all these different discoveries happening in parallel that will bring forward the next generation of vaccines and cures, and with things progressing at this speed I doubt anyone can predict just how far we will come in the next year.
Microsoft unveils Muse Generative AI Model for Video Game Prototyping
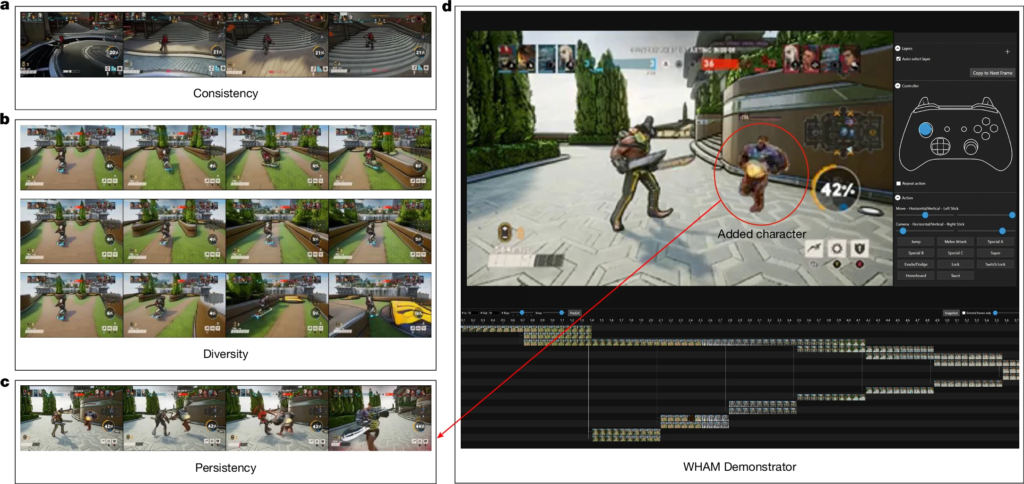
The News:
- Microsoft introduced Muse, a new generative AI model that can understand and simulate 3D game environments, physics, and player interactions. The model was developed by Microsoft Research in partnership with Xbox Game Studios’ Ninja Theory.
- Muse was trained on 1.6 billion parameters using approximately seven years of continuous human gameplay data from Ninja Theory’s multiplayer game Bleeding Edge.
- Muse can generate gameplay sequences up to two minutes long based on controller inputs and preprogrammed criteria, operating at a resolution of 300×180 pixels and Microsoft is already using Muse internally to develop real-time playable AI models using training data from other first-party Xbox Game Studios titles.
My take: This is pretty cool, but like we have seen on previous GenAI game generators the main question is what they can really be used for in practice? One suggestion from Microsoft is that it can be used to preserve classic game titles: “Thanks to this breakthrough, we are exploring the potential for Muse to take older back catalog games from our studios and optimize them for any device. We believe this could radically change how we preserve and experience classic games in the future and make them accessible to more players”. I’m not totally convinced myself, but hey it’s a cool model that’s trained on years of gameplay data that can produce a few minutes of tiny video animations, who knows where it will end up in a few years.
Read more:
OpenAI Introduces New Software Engineering Benchmark SWE-Lancer
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.12115
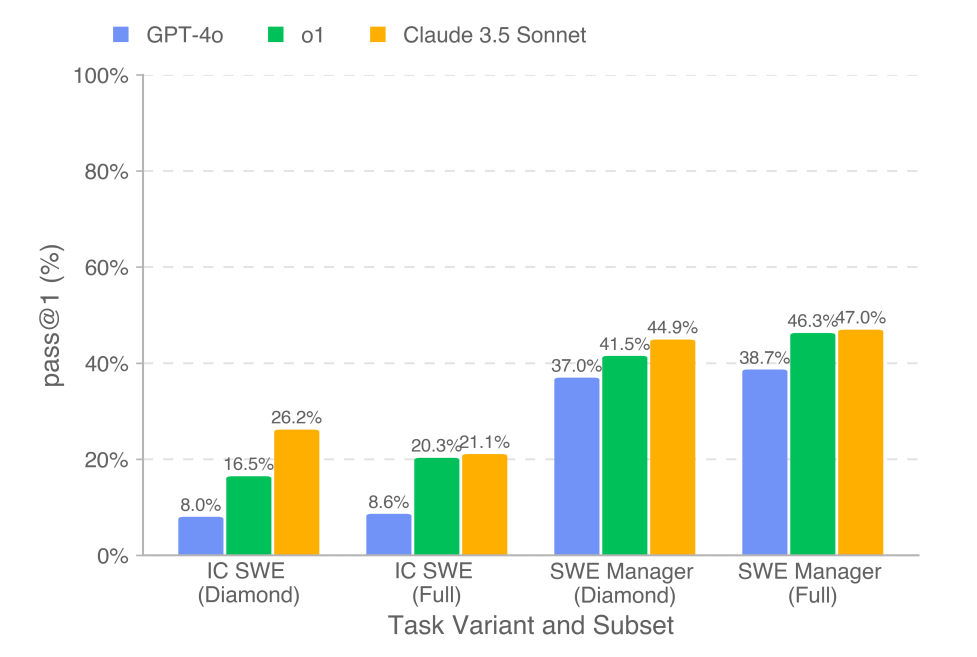
The News:
- OpenAI just introduced SWE-Lancer, a new benchmark designed to measure AI’s coding performance against real-world freelance software engineering jobs.
- SWE-Lancer features over 1,400 freelance software engineering tasks from Upwork, spanning from minor bug fixes to high-value feature implementations. The benchmark evaluates both coding and technical management decisions of LLMs, challenging them to write code and select engineering proposals.
- SWE-Lancer introduces monetary metrics, with success measured by how much a model could theoretically “earn” by completing tasks correctly. All top models struggled on the benchmark, with Claude 3.5 Sonnet performing best – solving nearly half of the tasks and earning $400k out of the $1M.
My take: I am not surprised that Claude 3.5 Sonnet is still the top performing programming model, even if it is now almost 8 months old. I have very high hopes for Claude 4 coming this spring, even if it’s just 20-30% better than Claude 3.5 those percentages will make all the difference in the world to a model that’s already amazingly good. This test is interesting since it puts autonomous AI agents in direct competition with freelance developers, and this is a battle that will not end well for the developers.
Perplexity Remakes DeepSeek-R1 Reasoning Model
https://www.perplexity.ai/hub/blog/open-sourcing-r1-1776
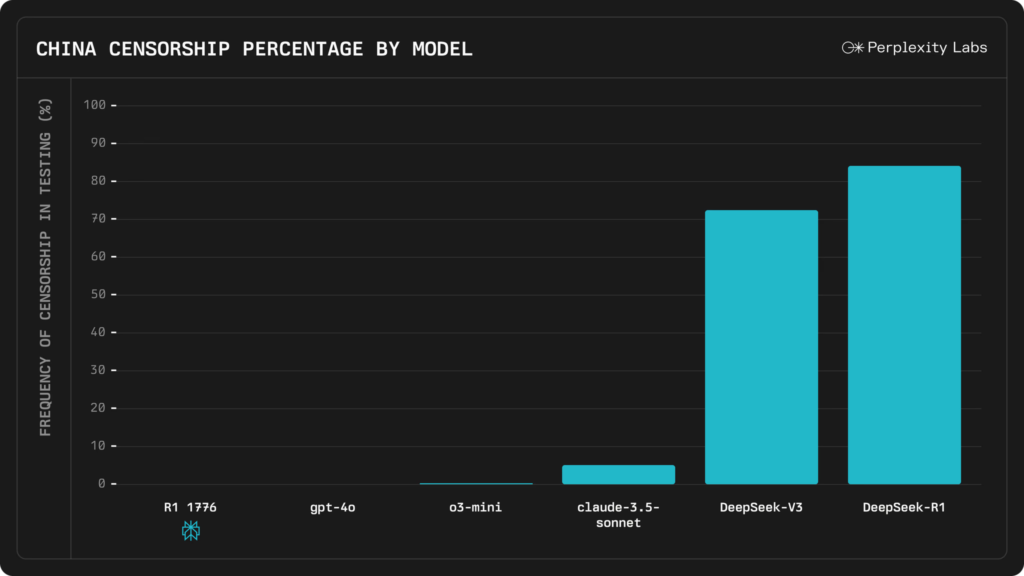
The News:
- Perplexity just released R1 1776, an open weight, MIT-licensed version of the DeepSeek-R1 model fine-tuned to provide accurate information on topics censored by the Chinese government.
- Perplexity used human experts to identify approximately 300 topics known to be censored by the CCP. They then used a dataset of 40,000 prompts around these 300 topics to retrain the model, aiming to maintain its chain-of-thought reasoning capabilities while removing built-in censorship.
- The new model is available through Perplexity’s Sonar API and as an open-source release on HuggingFace, making it accessible to developers and researchers.
My take: Wow, just look at that graph! Not only is the new model way less censored than DeepSeek V3 and R1, it’s also less censored than Claude 3.5 Sonnet! In tests done by Perplexity the model retains all it’s performance in benchmarks, but is now able to properly answer questions that in China are sensitive enough so that they are not included in the original training data. I know many companies that are already using DeepSeek R1 on-premise and I am quite sure most of these will switch over to R1 1776 as soon as possible.
Pika Labs Launches Pikaswaps – Video Object Replacement Tool
https://twitter.com/pika_labs/status/1892620122818294109

The News:
- Pikaswaps is a new AI video editing tool that lets users replace any object, character, or background in videos using text prompts or reference images while maintaining natural motion and lighting.
- Pikaswaps processes up to 5 seconds of video at a time and provides real-time previews of modifications before finalizing changes. Users can select specific areas for replacement using brush tools and customize the intensity of the swap effect to achieve desired results
- The system preserves motion consistency, lighting, and perspective when swapping elements, ensuring seamless integration of new content. Common applications include character customization, face swaps, outfit changes, and brand-specific content modifications for marketing purposes.
My take: Pika Labs just keep on releasing amazing new tools! 2025 Week 7 this year we got Pikadditions, 2024 Week 41 last year we got Pikaffects, and now we have Pikaswaps. This one is the most crazy yet, replace anything in the video with whatever you like. If you have a minute to spare go watch their launch video it’s worth the time.
Sakana AI Releases AI CUDA Engineer – 100x Faster Turned Out to be 3x Slower
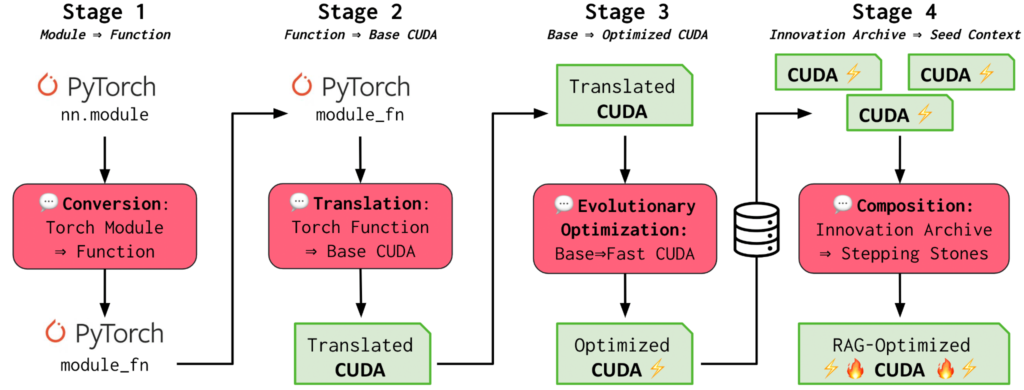
The News:
- This week, Sakana AI, an Nvidia-backed startup that’s raised hundreds of millions of dollars from VC firms, made a remarkable claim. The company said it had created an AI system, the AI CUDA Engineer, that could effectively speed up the training of certain AI models by a factor of up to 100x.
- However, users on X quickly discovered that Sakana’s system actually resulted in worse-than-average model training performance. According to one user, Sakana’s AI resulted in a 3x slowdown – not a speedup.
- Sakana published a postmortem on Friday admitting that the system found a way to “cheat” (as Sakana described it).
My take: This and the messy Grok 3 launch are my weekly reminders why I keep doing my newsletter. Instead of rushing, debating, discussing and posting about all the news on a daily basis, I reflect, research, and summarize what I find. I only posted about the Sakana AI CUDA Engineer in case any of you saw the original launch and was amazed at the incredible performance. In practice it turns out that it is actually quite difficult to automate the complex process of CUDA kernel optimization, which typically requires highly specialized expertise.
